Custom Annotation View
Add a custom annotation view
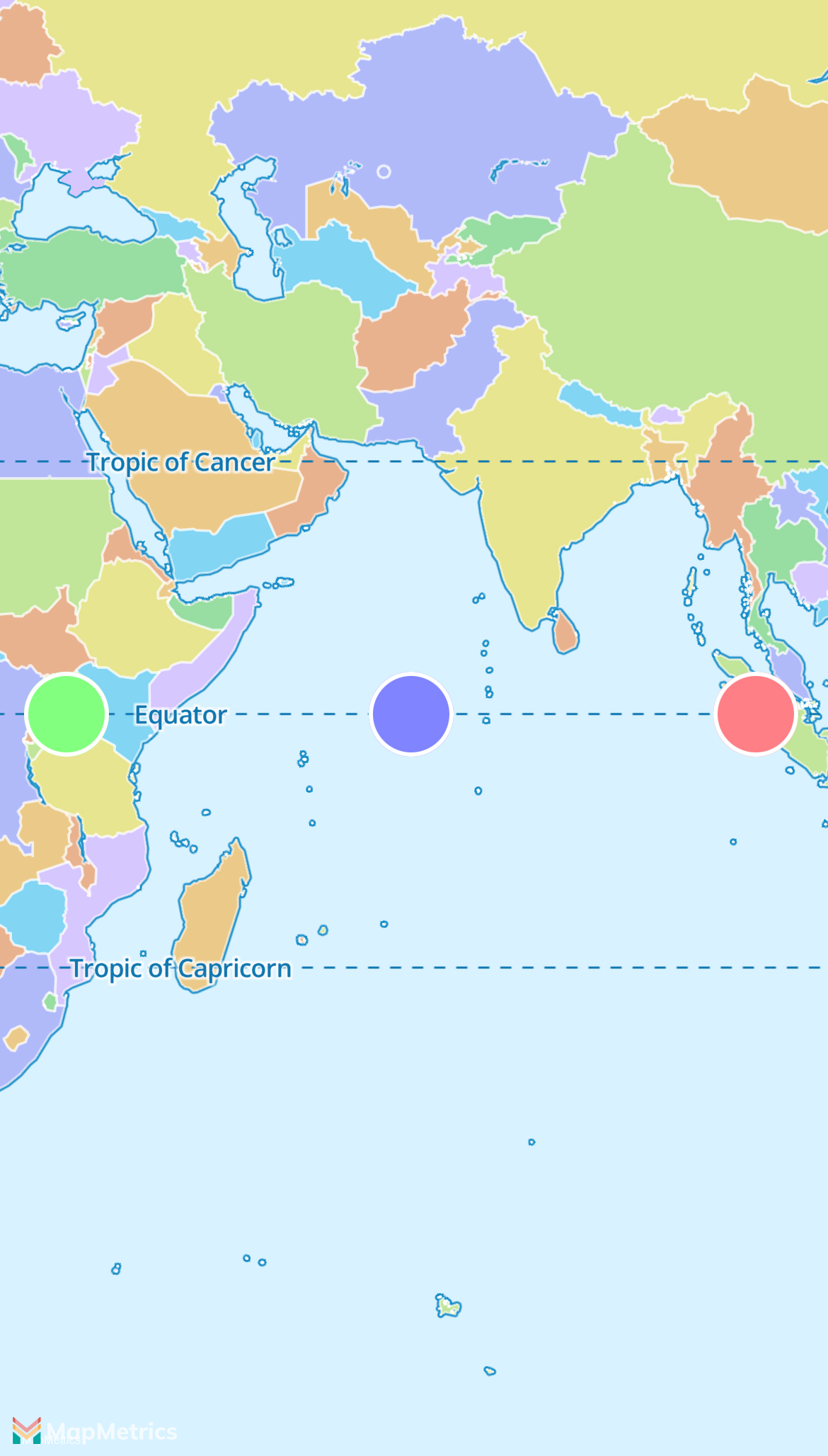
This examples shows how you can implement and use a custom MLNAnnotationView.
You need to implement MLNMapViewDelegate/mapView:viewForAnnotation: of MLNMapViewDelegate which will be called when you add an MLNAnnotation to the example. In this case, three MLNPointAnnotations are added to the map. When one is selected selected MLNAnnotationView/setSelected:animated: will be called.
swift
class AnnotationViewExample: UIViewController, MLNMapViewDelegate {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let mapView = MLNMapView(frame: view.bounds)
mapView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight]
mapView.attributionButton.isHidden = true
mapView.tintColor = .lightGray
mapView.centerCoordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 0, longitude: 66)
mapView.zoomLevel = 2
mapView.delegate = self
view.addSubview(mapView)
// Specify coordinates for our annotations.
let coordinates = [
CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 0, longitude: 33),
CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 0, longitude: 66),
CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 0, longitude: 99),
]
// Fill an array with point annotations and add it to the map.
var pointAnnotations = [MLNPointAnnotation]()
for coordinate in coordinates {
let point = MLNPointAnnotation()
point.coordinate = coordinate
point.title = "\(coordinate.latitude), \(coordinate.longitude)"
pointAnnotations.append(point)
}
mapView.addAnnotations(pointAnnotations)
}
// MARK: - MLNMapViewDelegate methods
// This delegate method is where you tell the map to load a view for a specific annotation. To load a static MLNAnnotationImage, you would use `-mapView:imageForAnnotation:`.
func mapView(_ mapView: MLNMapView, viewFor annotation: MLNAnnotation) -> MLNAnnotationView? {
// This example is only concerned with point annotations.
guard annotation is MLNPointAnnotation else {
return nil
}
// Use the point annotation’s longitude value (as a string) as the reuse identifier for its view.
let reuseIdentifier = "\(annotation.coordinate.longitude)"
// For better performance, always try to reuse existing annotations.
var annotationView = mapView.dequeueReusableAnnotationView(withIdentifier: reuseIdentifier)
// If there’s no reusable annotation view available, initialize a new one.
if annotationView == nil {
annotationView = CustomAnnotationView(reuseIdentifier: reuseIdentifier)
annotationView!.bounds = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: 40, height: 40)
// Set the annotation view’s background color to a value determined by its longitude.
let hue = CGFloat(annotation.coordinate.longitude) / 100
annotationView!.backgroundColor = UIColor(hue: hue, saturation: 0.5, brightness: 1, alpha: 1)
}
return annotationView
}
func mapView(_: MLNMapView, annotationCanShowCallout _: MLNAnnotation) -> Bool {
true
}
}
//
// MLNAnnotationView subclass
class CustomAnnotationView: MLNAnnotationView {
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
// Use CALayer’s corner radius to turn this view into a circle.
layer.cornerRadius = bounds.width / 2
layer.borderWidth = 2
layer.borderColor = UIColor.white.cgColor
}
override func setSelected(_ selected: Bool, animated: Bool) {
super.setSelected(selected, animated: animated)
// Animate the border width in/out, creating an iris effect.
let animation = CABasicAnimation(keyPath: "borderWidth")
animation.duration = 0.1
layer.borderWidth = selected ? bounds.width / 4 : 2
layer.add(animation, forKey: "borderWidth")
}
}